What is the contributing factor to digital divide?
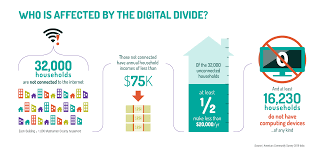
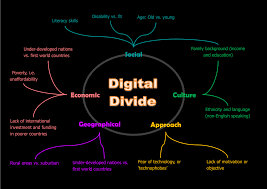
Digital divide refers to the gap between individuals and communities who have access to digital technologies and those who do not. It is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors, including socioeconomic status, geographic location, and age. One of the most significant contributing factors to the digital divide is income inequality. High-speed internet, computers, and other digital technologies can be expensive, making it difficult for low-income households to afford them. This creates a digital divide, where individuals and families with fewer resources are at a disadvantage compared to their wealthier counterparts who have better access to technology.
Geographic location is another factor contributing to the digital divide. People who live in rural or remote areas may have limited access to high-speed internet, and the infrastructure to support it may not be in place. This means that even if individuals have the financial means to purchase technology, they may not have the necessary connectivity to make use of it. Similarly, people living in urban areas may face barriers to technology access due to lack of infrastructure, such as areas with poor broadband coverage or low-quality internet connections.
Age is another contributing factor to the digital divide. Older adults may not have grown up with digital technology or had the opportunity to learn about it, making them less likely to have the skills and knowledge needed to use digital technologies. This can result in social isolation and exclusion, as well as decreased access to essential services and information that are increasingly only available online. In contrast, younger generations who grew up with digital technology have a greater level of comfort and familiarity with digital tools and are better positioned to benefit from them.


How do you reduce digital divide globally and locally?
Reducing the digital divide globally and locally requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the various contributing factors. One of the most effective ways to reduce the digital divide is to improve internet connectivity and infrastructure. Governments and private organizations can invest in building the necessary infrastructure, such as fiber-optic cables, to ensure high-speed internet access is available in all regions. This can also include expanding Wi-Fi networks, increasing mobile broadband access, and providing subsidies or financial assistance to low-income households to help them afford internet access and digital devices.
Another critical approach to reducing the digital divide is to improve digital literacy and education. Governments and organizations can provide training and resources to help individuals and communities develop the skills and knowledge they need to use digital technologies effectively. This includes providing training in basic computer skills, online safety, and digital citizenship. By equipping people with the necessary digital skills, they can better access job opportunities, education, and essential services available online.
Finally, reducing the digital divide requires addressing the socioeconomic factors that contribute to the divide. Governments and organizations can implement policies and programs that reduce income inequality, such as increasing the minimum wage, providing financial assistance to low-income households, and creating job opportunities that require digital skills. Additionally, providing access to digital tools and resources in public spaces such as libraries, community centers, and schools can also help bridge the digital divide for people who cannot afford digital devices and internet access at home.
How is there computer bias?
Computer bias refers to the systemic and inherent biases present in the design, development, and use of computer systems and algorithms. These biases can result in discriminatory outcomes, perpetuating existing social and economic inequalities. Computer bias can be unintentional, resulting from the lack of diversity among designers, developers, and users of technology. It can also be intentional, resulting from the perpetuation of harmful stereotypes and discriminatory attitudes.
One way that computer bias manifests is through algorithmic bias. Algorithms are designed to make decisions and predictions based on patterns in data. However, if the data used to train algorithms are biased, the resulting algorithms can perpetuate and amplify those biases. This can result in discriminatory outcomes, such as biased hiring or lending decisions, that disproportionately affect marginalized groups.
Another way that computer bias manifests is through design bias. Computer systems are designed with certain assumptions and biases in mind, such as assuming that users are able-bodied, English-speaking, or have certain cultural backgrounds. This can result in exclusionary design that makes it difficult or impossible for some groups to use technology effectively. For example, the lack of accessibility features in digital devices can make it challenging for people with disabilities to use them.