What is the concept of crowdsourcing?
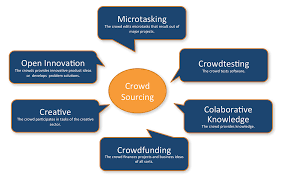
Crowdsourcing is the practice of obtaining information, ideas, or services from a large, undefined group of people, typically through the internet. It is a way of leveraging the collective intelligence and creativity of the crowd to solve problems or complete tasks that would be difficult or expensive to accomplish using traditional methods. Crowdsourcing can take many forms, such as crowdfunding, idea contests, and citizen science projects.
One of the key benefits of crowdsourcing is its ability to tap into the diverse perspectives and expertise of a large number of people. By allowing anyone to participate, crowdsourcing can generate a wide range of ideas and solutions that might not have been possible through traditional means. This can lead to more innovative and effective solutions, as well as greater community engagement and participation.
Crowdsourcing can be used in a variety of contexts, including business, government, and non-profit organizations. For example, businesses can use crowdsourcing to gather feedback from customers or to generate new product ideas. Governments can use crowdsourcing to engage citizens in the decision-making process and to collect data on community issues. Non-profits can use crowdsourcing to mobilize volunteers and donors or to crowdsource solutions to social and environmental problems.

How does computing raise legal and ethical issues?
Computing has the potential to raise significant legal and ethical issues. As technology continues to evolve, it is important to consider the potential consequences of new innovations and how they may impact society as a whole. One major area of concern is data privacy and security. With the increasing amount of personal information that is collected, stored, and shared online, there is a growing need for regulations and safeguards to protect individuals from data breaches, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime.
Another area of concern is the potential for computing to perpetuate existing biases and inequalities. As discussed earlier, computer bias can result in discriminatory outcomes that disproportionately affect marginalized groups. It is important to ensure that the development and use of technology is inclusive and equitable, and that it does not perpetuate or amplify existing social and economic inequalities.
Finally, computing can raise ethical issues around the use of artificial intelligence and automation. As AI becomes more advanced and ubiquitous, there is a growing need to consider the potential consequences of AI systems that can make decisions on their own, without human input or oversight. This includes issues around accountability, transparency, and the potential for AI to be used for harmful or unethical purposes. It is important to ensure that AI systems are designed and used in a way that is consistent with ethical principles and that promotes the well-being of individuals and society as a whole.


What is safe computing?
Safe computing refers to the practice of using technology in a way that minimizes the risk of cyber threats, such as viruses, malware, and phishing attacks. Safe computing includes a range of practices, such as keeping software up to date, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious emails and websites. By following safe computing practices, individuals and organizations can protect their personal and sensitive information, as well as prevent cyber attacks that can lead to financial loss, reputation damage, and other harmful outcomes.
One of the most important aspects of safe computing is keeping software and operating systems up to date. Updates often include security patches and other measures to protect against known vulnerabilities and cyber threats. It is also important to use anti-virus and anti-malware software to protect against known threats, and to avoid downloading software or clicking on links from unknown sources.
Another important aspect of safe computing is using strong passwords and protecting them from unauthorized access. This includes using a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols, as well as avoiding common words or phrases. It is also important to avoid using the same password for multiple accounts, and to use two-factor authentication whenever possible to provide an extra layer of protection.

